C# - Common Security Threats & Vulnerabilities (Part 3/6)
9. Insecure URL Redirect
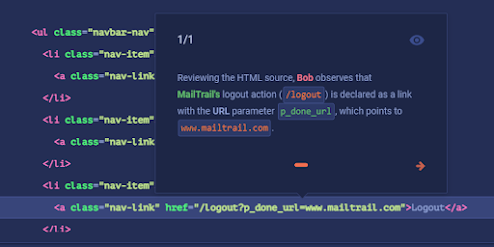
Insecure URL redirects or Unvalidated redirects are web attacks that cause the web application to redirect or forward an unsuspecting user to a malicious domain controlled by an attacker. These vulnerabilities commonly occur when a web application accepts untrusted input that could cause the web application to redirect the request to a URL contained within the untrusted input. By modifying the URL parameter input to a malicious site, a potential attacker can trigger a redirection to an arbitrary external domain and further facilitate phishing attacks against the users of the application.
For testing, Bob replaces the p_done_url value from www.mailtrail.com with Google's domain www.google.com and submits the following URL in his browser:
https://www.mailtrail.com/logout?p_done_url=https://www.google.com
Upon submitting the modified Logout URL, Bob is logged out from MailTrail service and redirected to Google's website.
Bob send an email to Alice:
Alice click the URL, she will be redirected to Bob's malicious website www.mail-trail.com with a fake login form.
Mitigation
To mitigate the risk of malicious actors exploiting URL redirects in the way that Bob did, application developers must always verify the URL that the user will be redirected or forwarded to, especially if the URL parameter can be changed or tampered on the client-side. This is especially important for applications that use dynamic content, such as web pages, that are not hosted by a single domain.
However, in our example, we can eliminate the need to perform URL verification by performing a server-side hostname lookup to securely redirected the user to the login webpage.
10. XML Entity Injection
XML External Entity (XXE) Injection is an attack targeting applications that transmit data between browser and server in XML format. By intercepting and modifying the data, an attacker can exploit potentially dangerous features of standard XML libraries, such as the parsing and loading of external entities, in order to gain access to the server's filesystem or to interact with backend systems that the application has access to.
Since the Upload and Sync Your Activities feature accepts XML formatted GPX documents, Bob decides to perform an XML External Entity (XXE) injection attack against the PeakFitness application.
XXE injection is a well-known XML attack that exploits the parsing of untrusted XML entities by a weakly configured XML parser, allowing an attacker to view arbitrary files on the application server filesystem.
Interesting! By simply, adding an external entity via the file syntax, Bob manages to trick PeakFitness's server-side XML parser to process the injected entity and loading the contents of the /etc/passwd file.
Mitigation
Developers must configure their applications XML parsers to disable the parsing of XML eXternal Entities (XXE) and Document Type Definitions (DTD) when parsing XML documents.
11. Clickjacking
Upon loading Bob's malicious webpage, Alice is presented with a cookie consent banner which requires her to confirm her consent by clicking the Accept button.













No comments: